Treatment Of Achilles Tendonitis
Overview
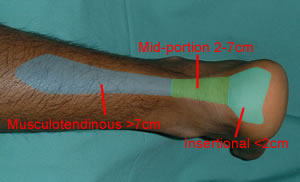 Achilles tendonitis is a condition of irritation and inflammation of the large tendon in the back of the ankle. Achilles tendonitis is a common injury that tends to occur in recreational athletes. Overuse of the Achilles tendon can cause inflammation that can lead to pain and swelling. Achilles tendonitis is differentiated from another common Achilles tendon condition called Achilles tendinosis. Patients with Achilles tendinosis have chronic Achilles swelling and pain as a result of degenerative, microscopic tears within the tendon.
Achilles tendonitis is a condition of irritation and inflammation of the large tendon in the back of the ankle. Achilles tendonitis is a common injury that tends to occur in recreational athletes. Overuse of the Achilles tendon can cause inflammation that can lead to pain and swelling. Achilles tendonitis is differentiated from another common Achilles tendon condition called Achilles tendinosis. Patients with Achilles tendinosis have chronic Achilles swelling and pain as a result of degenerative, microscopic tears within the tendon.
Causes
Achilles tendonitis is aggravated by activities that repeatedly stress the tendon, causing inflammation. In some cases even prolonged periods of standing can cause symptoms. In many people who have developed achilles tendonitis, chronic shortening of the gastroc-soleus muscle complex is the reason that home remedies and anti-inflammatory medications fail. In these instances the muscle itself becomes shortened and creates a constant stress at the tendon?s attachment. Like a green branch that is slowly bent, eventually it begins to breakdown. Over a prolonged period the tendon becomes inflamed, and in the worst cases, appears swollen and thickened. In certain circumstances attempts to heal have failed and the body?s inability to heal the tissue results in degenerative changes known as achilles tendonosis. Anti-inflammatory medication, stretching and ice may only provide temporary relief, because they address the inflammation but not the root cause.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of Achilles tendinitis include, pain and stiffness along the Achilles tendon in the morning, pain along the tendon or back of the heel that worsens with activity, Severe pain the day after exercising, thickening of the tendon, bone spur (insertional tendinitis) swelling that is present all the time and gets worse throughout the day with activity, If you have experienced a sudden "pop" in the back of your calf or heel, you may have ruptured (torn) your Achilles tendon. See your doctor immediately if you think you may have torn your tendon.
Diagnosis
A doctor examines the patient, checking for pain and swelling along the posterior of the leg. The doctor interviews the patient regarding the onset, history, and description of pain and weakness. The muscles, tissues, bones, and blood vessels may be evaluated with imaging studies, such as X-ray, ultrasound, or MRI.
Nonsurgical Treatment
Treatment of Achilles tendonitis begins with resting the tendon to allow the inflammation to settle down. In more serious situations, adequate rest may require crutches or immobilization of the ankle. Learn more about different treatments for Achilles tendonitis, including ice, medications, injections, and surgery.

Surgical Treatment
If non-surgical treatment fails to cure the condition then surgery can be considered. This is more likely to be the case if the pain has been present for six months or more. The nature of the surgery depends if you have insertional, or non-insertional disease. In non-insertional tendonosis the damaged tendon is thinned and cleaned. The damage is then repaired. If there is extensive damage one of the tendons which moves your big toe (the flexor hallucis longus) may be used to reinforce the damaged Achilles tendon. In insertional tendonosis there is often rubbing of the tendon by a prominent part of the heel bone. This bone is removed. In removing the bone the attachment of the tendon to the bone may be weakened. In these cases the attachment of the tendon to the bone may need to be reinforced with sutures and bone anchors.
Prevention
Stretching of the gastrocnemius (keep knee straight) and soleus (keep knee bent) muscles. Hold each stretch for 30 seconds, relax slowly. Repeat stretches 2 - 3 times per day. Remember to stretch well before running strengthening of foot and calf muscles (eg, heel raises) correct shoes, specifically motion-control shoes and orthotics to correct overpronation. Gradual progression of training programme. Avoid excessive hill training. Incorporate rest into training programme.
 Achilles tendonitis is a condition of irritation and inflammation of the large tendon in the back of the ankle. Achilles tendonitis is a common injury that tends to occur in recreational athletes. Overuse of the Achilles tendon can cause inflammation that can lead to pain and swelling. Achilles tendonitis is differentiated from another common Achilles tendon condition called Achilles tendinosis. Patients with Achilles tendinosis have chronic Achilles swelling and pain as a result of degenerative, microscopic tears within the tendon.
Achilles tendonitis is a condition of irritation and inflammation of the large tendon in the back of the ankle. Achilles tendonitis is a common injury that tends to occur in recreational athletes. Overuse of the Achilles tendon can cause inflammation that can lead to pain and swelling. Achilles tendonitis is differentiated from another common Achilles tendon condition called Achilles tendinosis. Patients with Achilles tendinosis have chronic Achilles swelling and pain as a result of degenerative, microscopic tears within the tendon.
Causes
Achilles tendonitis is aggravated by activities that repeatedly stress the tendon, causing inflammation. In some cases even prolonged periods of standing can cause symptoms. In many people who have developed achilles tendonitis, chronic shortening of the gastroc-soleus muscle complex is the reason that home remedies and anti-inflammatory medications fail. In these instances the muscle itself becomes shortened and creates a constant stress at the tendon?s attachment. Like a green branch that is slowly bent, eventually it begins to breakdown. Over a prolonged period the tendon becomes inflamed, and in the worst cases, appears swollen and thickened. In certain circumstances attempts to heal have failed and the body?s inability to heal the tissue results in degenerative changes known as achilles tendonosis. Anti-inflammatory medication, stretching and ice may only provide temporary relief, because they address the inflammation but not the root cause.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of Achilles tendinitis include, pain and stiffness along the Achilles tendon in the morning, pain along the tendon or back of the heel that worsens with activity, Severe pain the day after exercising, thickening of the tendon, bone spur (insertional tendinitis) swelling that is present all the time and gets worse throughout the day with activity, If you have experienced a sudden "pop" in the back of your calf or heel, you may have ruptured (torn) your Achilles tendon. See your doctor immediately if you think you may have torn your tendon.
Diagnosis
A doctor examines the patient, checking for pain and swelling along the posterior of the leg. The doctor interviews the patient regarding the onset, history, and description of pain and weakness. The muscles, tissues, bones, and blood vessels may be evaluated with imaging studies, such as X-ray, ultrasound, or MRI.
Nonsurgical Treatment
Treatment of Achilles tendonitis begins with resting the tendon to allow the inflammation to settle down. In more serious situations, adequate rest may require crutches or immobilization of the ankle. Learn more about different treatments for Achilles tendonitis, including ice, medications, injections, and surgery.

Surgical Treatment
If non-surgical treatment fails to cure the condition then surgery can be considered. This is more likely to be the case if the pain has been present for six months or more. The nature of the surgery depends if you have insertional, or non-insertional disease. In non-insertional tendonosis the damaged tendon is thinned and cleaned. The damage is then repaired. If there is extensive damage one of the tendons which moves your big toe (the flexor hallucis longus) may be used to reinforce the damaged Achilles tendon. In insertional tendonosis there is often rubbing of the tendon by a prominent part of the heel bone. This bone is removed. In removing the bone the attachment of the tendon to the bone may be weakened. In these cases the attachment of the tendon to the bone may need to be reinforced with sutures and bone anchors.
Prevention
Stretching of the gastrocnemius (keep knee straight) and soleus (keep knee bent) muscles. Hold each stretch for 30 seconds, relax slowly. Repeat stretches 2 - 3 times per day. Remember to stretch well before running strengthening of foot and calf muscles (eg, heel raises) correct shoes, specifically motion-control shoes and orthotics to correct overpronation. Gradual progression of training programme. Avoid excessive hill training. Incorporate rest into training programme.